Thyroglossal duct cyst CT image
Introducd:Thyroglossal duct cyst CT image
- Most common congenital anomaly of the neck
-
- 2-4% of all neck masses
- Over half present in the first decade of life but may also be seen in adults
- Pyramidal lobe of the thyroid is the most common remnant of the thyroglossal tract (50% of population)
- Etiology
-
- Represents a persistent epithelial tract during the descent of the thyroid from the foramen cecum to its final position in the anterior neck
- Normally this duct obliterates early in fetal life
- Histologically
-
- Well-defined cyst with an epithelial lining composed of either squamous or respiratory epithelium
- There can sometimes be islands of thyroid tissue lying in the walls of the cysts
- Cysts are filled with mucoid or mucopurulent material, depending on whether the cyst has been infected
- Types of thyroglossal duct cysts
-
-
Infrahyoid type
- 65% and is mostly found in the paramedian position
-
Suprahyoid type
- Nearly 20% and is positioned in the midline
-
Juxtahyoid cysts
- 15%
-
Intralingual location
- 2%
-
Suprasternal variety
- 10% of cases
-
Intralaryngeal
- Very rare
-
Infrahyoid type
- Clinical
-
- Nontender and mobile masses
-
Infected cysts may manifest as tender masses with
- Dysphagia
- Dysphonia
- Draining sinus
- Fever
- Enlarging neck mass
- Often appear after an upper respiratory tract infection
- Airway obstruction possible, especially with intralingual cysts
- The pathognomonic sign is that the cyst moves with tongue protrusion
- Imaging
-
- Ultrasound and CT scanning are the radiologic tools of choice
- Ultrasound is the gold standard
- Ultrasound can distinguish between solid and cystic components
- CT scanning may reveal a well-circumscribed cystic lesion, 2-4 cm in diameter with capsular enhancement
- Thyroid scanning may be done to rule out the cyst containing the only functioning thyroid tissue
- Differential diagnosis
-
- Dermoid cyst
- Lymphadenopathy
- Sebaceous cysts
- Schwannomas
- Lymphatic malformations
- Complications
-
- Infection is probably the most common complication
- Local growth and invasion is extremely uncommon
-
Carcinoma is extremely rare
- Occurs in about 1% to 2% of patients
-
Thyroid ectopia
- Fewer than 5% of these cysts actually have ectopic thyroid tissue
- Treatment
-
-
Surgical treatment of choice for thyroglossal cysts is the Sistrunk operation
- Includes dissection of the hyoid bone and the base of the tongue
- Recurrence is approximately 3-5% and is increased by incomplete excision and a history of recurrent infections
- Thyroid suppression therapy is done by many practitioners
- Recurrence is the most common complication and is managed with a central neck dissection
-
Surgical treatment of choice for thyroglossal cysts is the Sistrunk operation
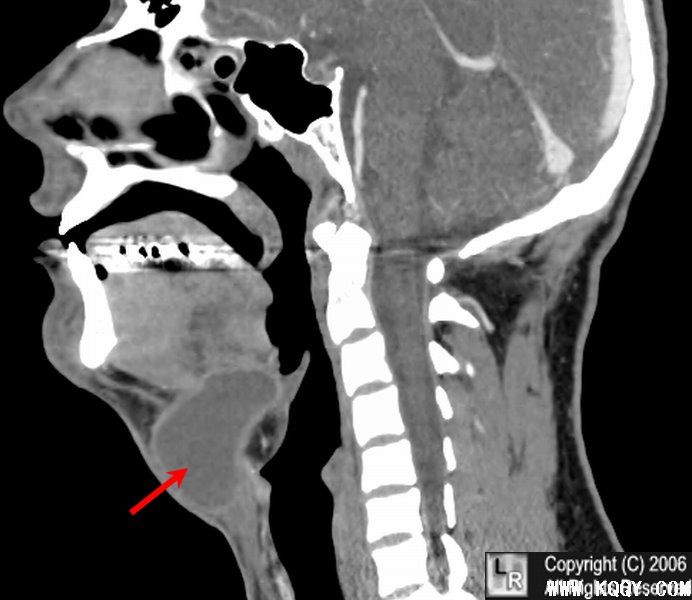
Thyroglossal duct cyst . Reconstructed CT scan of the neck demonstrates a midline cystic
lesion (red arrow) with a slightly enhancing wall. The contents measured fluid density.
TAGS:
0% (0)
0% (10)
Sponsored Links
Daliy Dental Topics
Useful Links
- Long Island College Hospital - [education]
- Faculty of Dental Medicine - H [education]
- The American Association of Or [organize]
- Summer Institute in Clinical D [organize]
- Academy of Osseointegration [organize]
- University of North Carolina a [education]
- American Orthodontic Society [article]
- American Equilibration Society [article]
- Niigata University - Japan [education]
- University of Buffalo [education]